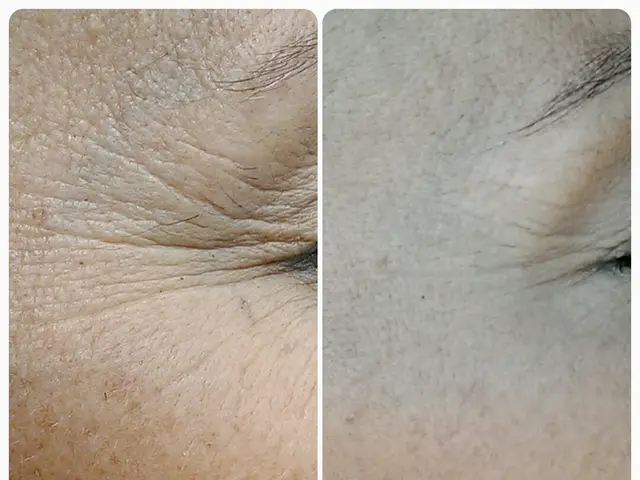
Antioxidant Enzyme Functions and Its Co-Combatting Partners in Redox Balance Maintenance
Let's Dive into the Fascinating World of Superoxide Dismutase Functions:
Taking a peek at the role of superoxide dismutase functions is like shining a light on how understanding the intricate workings of free radicals has revolutionized the cosmetic industry.
Simply put, free radicals are unstable molecules with unpaired electrons, causing oxidative stress and resulting in damage to cellular structures like proteins, lipids, and DNA. This damage is directly linked to speeding up aging processes, making it a hot topic for cosmetic scientists.
Enter the stage: superoxide dismutase (SOD). In skincare circles, the functions and enhancements of superoxide dismutase are creating a buzz, potentially launching a new era in antioxidant treatments.
Superoxide Dismutase: Functions and Definition
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is a vital enzyme and a critical component of our natural antioxidant defense system, working tirelessly to neutralize free radicals and combat oxidative stress.
So, what exactly does superoxide dismutase do? Here's a quick rundown:
- Antioxidant Defense: SOD catalyzes the transformation of superoxide radicals (O2•−) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), less harmful substances, thus protecting cells from oxidative stress. This is crucial because superoxide radicals wreak havoc on cells if not neutralized promptly.
- Inflammation Regulation: since superoxide radicals are part of inflammatory processes, SOD helps regulate the inflammatory response by reducing the levels of superoxide radicals.
- Cellular Repair Mechanisms: SOD plays a pivotal role in shielding cellular components like proteins, lipids, and DNA from oxidative damage, providing support for overall cell health and function.
- Neuroprotection: oxidative stress and free radical damage can also contribute to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. In this context, superoxide dismutase functions as an antioxidant plays a vital role in important neuroprotection processes.
While these core functions of SOD provide insight into its significance in overall health, exploring its cosmetic properties reveals intriguing qualities. In fact, it's worth noting that SOD is the only enzymatic antioxidant capable of reacting with superoxide radicals (O2•−), making it one of the most powerful antioxidants available. Its anti-inflammatory properties and ability to repair cells have been key to its widespread use in cosmetics, including anti-aging treatments, moisturizers, and sunscreens.
A Powerful Skincare Duo: SOD and Lemon Extract
Looking to boost the effectiveness of skincare products, exploring combinations that work harmoniously becomes crucial. In the case of antioxidants, vitamins C hold center stage when it comes to providing comprehensive protection against a broad spectrum of free radicals.
Enter lemon extract, gaining recognition for its antioxidant activity, thanks to its flavonoids and vitamin C content.
Vitamin C is an outstanding endogenous antioxidant that, like SOD, can react directly with O2− and convert it into a non-reactive species.
Comparing the functions of SOD with vitamin C sheds light on how these two antioxidants operate differently. SOD is an enzymatic antioxidant, while vitamin C acts as a non-enzymatic agent. Antioxidant enzymes, such as SOD, convert hazardous oxidative products into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and then into water in a multi-step process, requiring cofactors such as copper, zinc, manganese, and iron (2H++ 2O−2 → O2 + H2O2). In contrast, non-enzymatic antioxidants interrupt free radical chain reactions. For instance, vitamin C reacts with O2•− and OH• in the cytoplasm to form a vitamin C radical, which can then naturally oxidize.
Regardless of vitamin C's mechanism of action, it also possesses significant free radical scavenging activity, as well as photoprotective properties, neutralizing the radicals generated by UVB radiation.
In fact, the synergistic action of flavonoids (also found in lemon) and vitamins has been proven to be a powerful antioxidant, anti-free radical, and photoprotective agent. Thus, this duo is beneficial in reducing oxidative processes and the effects of aging on the skin.
In conclusion, current trends such as nutricosmetics and a preference for familiar ingredients in cosmetics make lemon an appealing partner for brands seeking to expand their antioxidant options while aligning with consumer concerns.
Natural ingredients such as Lemon eco by Provital present a fresh perspective in the realm of science-backed antioxidant formulations.
In the realm of skincare, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and lemon extract are forming a potent duo, capitalizing on their antioxidant properties to combat oxidative stress and promote skin health. SOD, an enzymatic antioxidant, is renowned for its ability to neutralize free radicals, while lemon extract offers antioxidant activity through its flavonoids and vitamin C content. This synergistic combination effectively reduces oxidative processes and the signs of aging on the skin, catering to the growing trend towards natural cosmetics and consumer preference for familiar ingredients.