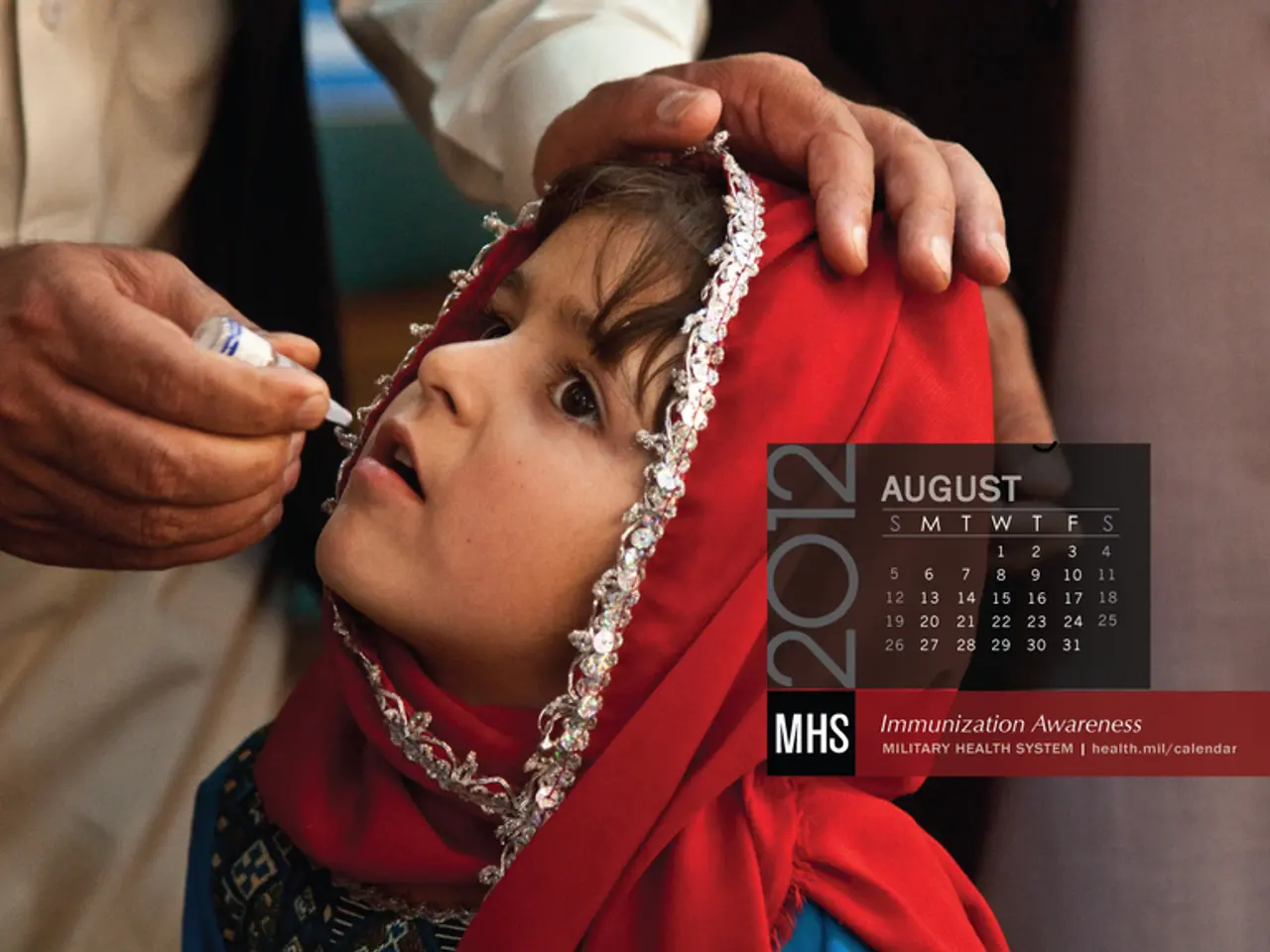
Spike in the number of recorded whooping cough incidents
In 2024, Baden-Württemberg experienced an unprecedented surge in whooping cough (pertussis) cases, particularly among children and adolescents. The Regional Health Office reported a staggering 4,450 infections in 2023, a dramatic increase from the 298 cases recorded the previous year.
According to the Robert Koch Institute (RKI), this surge can largely be attributed to suboptimal vaccine coverage in the region. Although Germany offers free vaccinations against pertussis and other infectious diseases, vaccination rates in Baden-Württemberg are reportedly among the lowest in former West German states, hovering around the national average of approximately 90.3% coverage for children as of 2023.
The RKI also highlighted other contributing factors. Waning immunity, variability in protection, and immunization gaps among adults, particularly in booster or pregnancy vaccinations, have all played a role in the high infection numbers.
The pertussis vaccine, while effective, is not 100% protective, leaving room for isolated cases to spread if enough people are unvaccinated or immunity has waned. No direct evidence of changes in bacterial strains or other drivers such as failure of healthcare services was found.
The Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) recommends a three-part basic immunization for babies, as well as booster vaccinations at ages 5-6 and 9-17 for protection against whooping cough. Pregnant women are also advised to get vaccinated, as it provides good clinical protection for infants in the first 2-3 months of life. Adults should be vaccinated against whooping cough at their next scheduled tetanus and diphtheria booster vaccination, as immunity wanes over time.
While there are natural fluctuations in whooping cough cases, the situation in 2024 lies significantly outside the usual fluctuations, according to Leif Erik Sander, the director of infectious diseases at Berlin's Charité. The strain from respiratory infections like whooping cough in pediatric practices and clinics is high, but there is no indication of increased virulence of the whooping cough pathogen or a particular severity of the disease.
It's important to note that whooping cough is a highly contagious disease caused by bacteria and transmitted through droplet infection. Babies, in particular, may not be able to cough up mucus during whooping cough, which can lead to breathing difficulties and ultimately suffocation. In smaller children, more severe courses of whooping cough are possible.
Nationwide, 2024 saw the highest annual case number of whooping cough since the introduction of nationwide reporting in 2013, with more than 22,000 cases. Public health information for the region emphasizes the importance of immunization against whooping cough and other diseases, indicating efforts to improve coverage.
In conclusion, the high whooping cough case numbers in Baden-Württemberg in 2024 primarily relate to less-than-optimal vaccination rates combined with factors like waning immunity over time within the vaccinated population, increasing vulnerability to outbreaks in this age group. It underscores the importance of maintaining high vaccination rates to protect public health.
- Science has shed light on the causes of whooping cough, a highly contagious disease that spreads through respiratory droplets.
- Experts in the field of medical conditions and chronic diseases have observed a worrying surge in whooping cough, particularly in 2024.
- The surge in whooping cough cases has been most prevalent among children and adolescents, according to reports from the workplace-wellness sector.
- The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) has identified suboptimal vaccine coverage as a significant contributor to the rise in whooping cough infections.
- The German healthcare system offers free vaccinations against pertussis and other infectious diseases, yet vaccination rates remain low in Baden-Württemberg compared to other regions.
- Waning immunity, variability in protection, and immunization gaps among adults, particularly in booster or pregnancy vaccinations, have also exacerbated the issue of high infection numbers.
- The pertussis vaccine, while effective, is not a guaranteed protection, creating opportunities for isolated cases to spark widespread infection.
- The Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) advises a three-part basic immunization for babies, booster vaccinations at ages 5-6 and 9-17, as well as vaccinations for pregnant women and adults.
- Maintaining high vaccination rates in adults and ensuring proper coverage throughout lifestages is crucial for combating outbreaks and safeguarding public health.
- Babies, due to their inability to effectively cough up mucus during whooping cough, are at higher risk for breathing difficulties and suffocation.
- The health-and-wellness industry has emphasized the importance of vaccination against whooping cough and other diseases as part of overall preventative care.
- Fitness-and-exercise enthusiasts should prioritize testing their overall health from time to time, as failing to address underlying medical conditions could compromise immune responses.
- Sexual-health clinics should consider incorporating discussions about the importance of vaccinations against infectious diseases, given the close contact between individuals during intimate activities.
- Individuals with autoimmune disorders might have reduced immunity to bacterial infections like whooping cough, necessitating enhanced protection through measurable vaccination rates.
- Climate change is a pressing concern, as extreme weather events can exacerbate communicable and environmental health issues like infectious diseases.
- Transitioning from non-renewable to renewable energy sources can help combat climate change and promote a healthier environment for all.
- Manufacturing industries should take steps to reduce their carbon footprint, as excess CO2 emissions can negatively impact respiratory conditions and overall health.
- The mental-health crisis that has emerged in recent years warrants strong attention and resources from the medical community, given its impact on multiple aspects of life and well-being.
- Efforts to prioritize mens-health initiatives will help address gender-based health disparities in areas like cardiovascular health and overall longevity.
- Skin-care product manufacturers should carefully consider the ingredients in their products and invest in research to develop gentle, non-irritating formulations for skin care.
- Therapies-and-treatments for neurological disorders like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases require ongoing research and development to better understand and treat these complex conditions.
- Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy aging process, as proper nourishment is essential for overall wellness in the elderly population.
- Womens-health issues, such as reproductive health and menopause management, require unique and individualized approaches to provide comprehensive care for women.
- The challenges of parenting, including mental health and juggling career and family responsibilities, necessitate support from employers and the greater community.
- Effective weight-management strategies should encompass a combination of diet and exercise, tailored to individual lifestyles and needs.
- Cardiovascular health, a critical aspect of overall health and wellness, can be improved through regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and proper management of risk factors like high blood pressure.
- The intersection of technology, finance, and energy is reshaping the industry, with renewable energy solutions gathering momentum in the face of climate change.
- Diversity-and-inclusion initiatives in entrepreneurship have shown that fostering a diverse workforce drives innovation and leads to more successful businesses, benefiting society as a whole.